Implementing actions in C++ context classes
In order to provide an action interface for C++ context class, an executeFunction() method has to be overloaded in the context class. When using the ClassEditor or Designer for implementing actions, it is sufficient marking a function as action in the function property list.
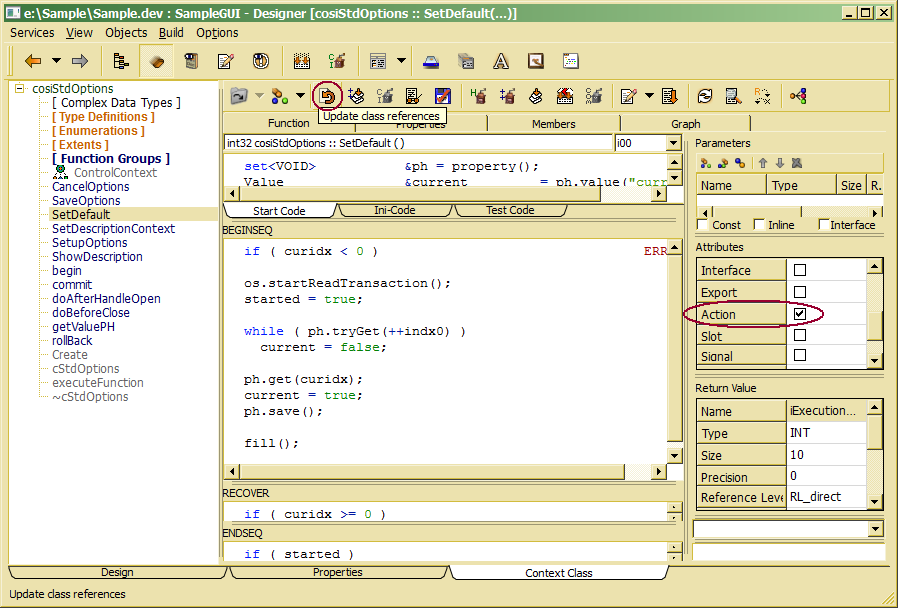
When clicking the Update class references tool bar button, an executeFunction() method will be created from for all functions marked as action.
When not using ODE tools, an action interface similar to the one below has to be provided "manually" by the context class programmer. There are no specific requirements, except that the action interface maps the action name to a function call but does not call the function when check only is required.
int32 cStdOptions :: executeFunction (odaba::String sName, bool bFunctionCheck )
{
using namespace odaba;
typedef int32 (cStdOptions::* context_function_pointer)();
typedef std::map<odaba::String,context_function_pointer> FunctionTable;
static FunctionTable function_table;
static bool initialized = false;
int32 iExecutionError = -1;
if ( !initialized ) {
function_table.insert(FunctionTable::value_type("CancelOptions",&cStdOptions::CancelOptions));
function_table.insert(FunctionTable::value_type("SaveOptions",&cStdOptions::SaveOptions));
function_table.insert(FunctionTable::value_type("SetDefault",&cStdOptions::SetDefault));
function_table.insert(FunctionTable::value_type("SetDescriptionContext",&cStdOptions::SetDescriptionContext));
function_table.insert(FunctionTable::value_type("SetupOptions",&cStdOptions::SetupOptions));
function_table.insert(FunctionTable::value_type("ShowDescription",&cStdOptions::ShowDescription));
initialized = true;
}
FunctionTable::iterator it = function_table.find(sName);
if ( it != function_table.end() ) {
iExecutionError = false;
if ( !bFunctionCheck )
iExecutionError = (this->*it->second)();
}
else
iExecutionError = ControlContext::executeFunction(sName,bFunctionCheck);
if ( iExecutionError == 1 && !bFunctionCheck )
message();
return(iExecutionError);
}

